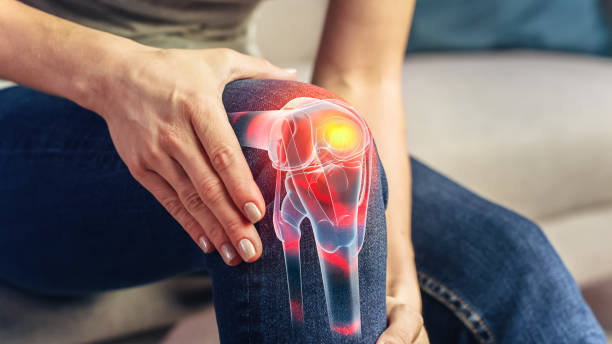
The knee is a complex joint that is composed of several bones, cartilage, ligaments, and tendons. Our knees serve the critical purpose of carrying our weight, maintaining our upright posture and enabling us to walk and stand. Injuries, diseases or age-related knee deterioration can be painful and debilitating for movement.
Knee replacement surgery, also known as knee arthroplasty is an orthopaedic procedure that involves removing the damaged or diseased part of the knee joint and replacing it with an artificial component.
When Might I Need Knee Replacement Surgery?
Knee replacement surgery is usually done for people who experience severe knee pain or immobility that is not relieved by other treatments such as medication, physical therapy, or lifestyle changes. The following are some of the most common conditions that might lead to knee replacement surgery:
- Osteoarthritis is the most common cause of knee pain and is caused by wear and tear of the cartilage that cushions the knee joint
- Rheumatoid arthritis is an autoimmune disease that causes inflammation of the synovial lining of the knee joint. The synovial lining produces synovial fluid that lubricates and nourishes a joint. Inflammation of the synovial lining leads to damage to the joint
- Post-traumatic arthritis is a type of arthritis that occurs after a knee injury, such as a fracture or ligament tear
- Avascular necrosis is a condition in which the bone tissue in the knee joint dies due to poor blood supply
- Knee deformities including conditions such as bowed legs or knock knees, which can lead to uneven wear and tear of the knee joint
- If failed previous knee surgery did not provide adequate relief, knee replacement surgery may be necessary
What Does Pre-Operative Care For Knee Replacement Surgery Look Like?
Your doctor will conduct a thorough medical evaluation to assess your overall health and determine if you are a good candidate for knee replacement surgery. This may involve testing your knee’s stability, strength and range of motion as well as blood tests, imaging scans (such as x-rays), and other diagnostic tests.
You may be advised to make lifestyle modifications before surgery, such as losing weight, quitting smoking, and increasing physical activity, to improve your overall health before the surgery and reduce the risk of complications after the surgery. You will likely also be referred to a physical therapist to help strengthen the muscles around the knee joint and improve mobility before surgery.
You will be given instructions on what to do before the surgery and what to expect on the day of surgery. You will also be asked to sign a consent form before the surgery, indicating that you understand the risks and benefits of knee replacement surgery and agree to undergo the procedure.
Your medical team will review any medications you might be on to determine if any of them need to be stopped or adjusted before surgery. In the days leading up to surgery, you will be instructed not to eat or drink anything after midnight the night before the procedure.
What Happens During Knee Replacement Surgery?
Knee replacement surgery usually takes several hours. You will be given general anaesthesia, which will put you to sleep during the procedure. The surgeon will make an incision over the knee to access the joint. The joint is prepared by removing the damaged cartilage and bone from the femur (the thigh bone) and tibia (the shin bone) using special surgical tools.
The implant, typically made of metal, plastic or a combination of both is then placed into the prepared bone. Implants can be placed with the use of bone cement or without cement depending on the type of implant. The surgeon may also resurface the patella (the kneecap), which means that the underside of the patella, which articulates with the femur and tibia, is replaced or covered with a smooth, artificial surface, which allows for a smooth movement against the adjoining bones.
The surgeon then closes the incision with stitches or staples and applies a sterile dressing. You will then be taken to a recovery room where you are monitored for a few hours before being transferred to a hospital room or discharged home. You might stay in the hospital for a few days after surgery, during which time you will be given pain medication to help manage any discomfort and undergo physical therapy to help you regain mobility.
What Does Post-Operative Care Look Like For Knee Replacement Surgery?
Proper post-operative care is crucial for a smooth recovery and to reduce complications after knee replacement surgery. Some common postoperative care steps include pain management, physical therapy exercises to strengthen muscles and improve mobility, wound care to prevent infection, wearing compression stockings and taking blood thinners to prevent blood clots. Follow-up appointments will be scheduled to monitor your progress and ensure proper healing.
From a practical perspective, it is a good idea to prepare your home to ensure that you have adequate support during recovery. This might involve ensuring that tasks within your daily routine are accessible and making arrangements for someone to help with daily tasks and transportation after surgery.
Your medications will be reviewed during follow-up visits to determine if any adjustments are necessary. It is essential to adhere to all of your care team’s instructions and to ask questions that may arise during the recovery process, to minimise complications and ensure proper healing.
What Are The Risks Of Knee Replacement Surgery?
Knee replacement surgery is a major procedure and carries risks, such as infection, blood clots, and nerve damage. Your surgeon will discuss the risks and benefits of the procedure with you before undergoing knee replacement surgery.
The Main Considerations For Knee Replacement Surgery
Knee replacement surgery is a complex orthopaedic procedure that involves removing the damaged or diseased part of the knee joint and replacing it with an artificial implant.
This surgery may be necessary for individuals who experience severe knee pain or immobility that is not relieved by other treatments. Proper preoperative and postoperative care is crucial to minimise complications and ensure proper healing. While knee replacement surgery carries some risks, it can greatly improve an individual's quality of life and mobility.
As always, it is important to discuss any concerns with your healthcare provider and to adhere to their instructions for a successful recovery.

 71–75 Shelton Street, Covent Garden, London, WC2H 9JQ
71–75 Shelton Street, Covent Garden, London, WC2H 9JQ +44 (0) 20 3376 1032
+44 (0) 20 3376 1032



