Pulmonology is a medical speciality that focuses on the respiratory system, which includes the lungs, airways, and associated structures that enable breathing and oxygen exchange in the body.
What Do Pulmonologists Do?
Pulmonologists specialise in managing chronic respiratory diseases, perform interventional procedures, and provide critical care in the ICU.
They actively contribute to research and play a vital role in educating healthcare professionals about respiratory conditions.
he Most Common Respiratory Conditions?
- Asthma
- Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease - a progressive lung disease that includes chronic bronchitis and emphysema
- Pneumonia
- Lung cancer
- Tuberculosis (TB)
- Pulmonary fibrosis
- Sleep apnea - interruptions in breathing during sleep
- Pulmonary embolism - a blockage of the pulmonary arteries
- Cystic fibrosis - genetic disorder that causes thick and sticky mucus production
- Occupational lung diseases
What Are The First Signs Of Lung Problems?
The early signs of lung problems can vary depending on the condition or disease. Experiencing the following symptoms doesn't necessarily mean you have a severe lung problem, but it's advisable to consult a healthcare professional for proper evaluation and diagnosis.
- Persistent cough: A cough lasting more than a few weeks or producing blood or excessive mucus.
- Shortness of breath: Feeling breathless or having difficulty breathing during physical activity or even at rest can indicate lung problems. It may manifest as not getting enough air or struggling to take deep breaths.
- Chest pain: Lung-related chest pain can vary in intensity and location. It may feel sharp, dull, or achy and can be exacerbated by coughing, deep breathing, or specific body positions.
- Wheezing: A high-pitched whistling sound produced during breathing, typically heard when exhaling, may indicate narrowing or blockage of the airways, such as asthma or COPD.
- Fatigue: Feeling excessively tired or lacking energy can be a symptom of lung problems. Reduced lung function can result in inadequate blood oxygenation, leading to fatigue and a decreased ability to perform usual activities.
- Recurrent respiratory infections: Frequent or recurring respiratory diseases, such as bronchitis or pneumonia, could suggest underlying lung issues.
- Unexplained weight loss: Significant and unexplained weight loss without diet or physical activity changes can be a potential sign of certain lung conditions, including lung cancer or tuberculosis.
- Clubbing of fingers: Clubbing is an abnormal enlargement of the fingertips and rounding of the nails. It can be associated with several lung diseases, such as lung cancer, bronchiectasis, or cystic fibrosis.
- Voice changes: A persistent hoarse voice may indicate a problem with the vocal cords or airways.
How Are Respiratory Conditions Diagnosed?
When you visit a pulmonologist, they perform tests and examinations to check your lung health, including:
- Asking about your medical history
- Conducting a physical examination to assess symptoms and risks.
- Lung function tests, like spirometry, to evaluate lung capacity and airflow.
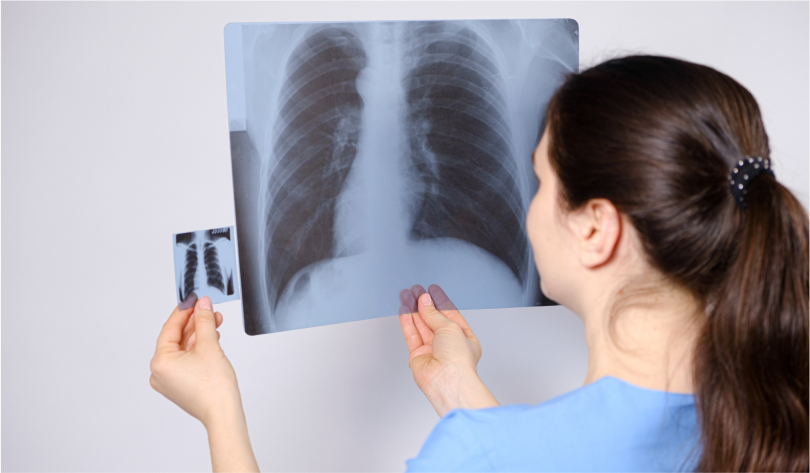
- Chest X-rays or CT scans to view detailed lung images.
- Bronchoscopy, if needed, to visualise airways and collect samples.
- Blood tests, such as arterial blood gas analysis, to assess respiratory function.
- Specialised tests based on symptoms, like exercise tests or genetic testing.
Frequently Asked Questions
Both terms encompass the same scope of practice and involve the study and care of the respiratory system.
- What is the exact diagnosis based on my symptoms and test results?
- What are the possible causes of my respiratory condition and can I take any preventive measures to reduce the risk of exacerbations or complications?
- What are the available treatment options for my condition, and what are their benefits and potential side effects?
- Are there any lifestyle modifications I should consider to improve my lung health?
- How will this condition progress over time, and what can I expect regarding symptom management and long-term prognosis?

 71–75 Shelton Street, Covent Garden, London, WC2H 9JQ
71–75 Shelton Street, Covent Garden, London, WC2H 9JQ +44 (0) 20 3376 1032
+44 (0) 20 3376 1032



