Suffering from long-term joint or muscular pain can have a debilitating effect on your life.
While there is no cure for most rheumatoid conditions, early diagnosis and appropriate treatment can help prevent your condition from deteriorating.
Which Conditions Are Treated By A Rheumatologist?
Rheumatologists diagnose and manage chronic inflammatory musculoskeletal conditions. These conditions include:
- Rheumatoid arthritis
- Psoriatic arthritis
- ankylosing spondylitis
- Osteoarthritis
- Lupus
- Scleroderma
- Myositis
- Osteoporosis
- Gout
- Musculoskeletal infections
- Sjögren’s syndrome (an immune disorder causing dry eyes and a dry mouth)
- Beçhet’s disease (causes blood vessel inflammation)
What Causes Rheumatic Autoimmune Diseases?
Autoimmune disease happens when your body's natural defence system (your immune system) cannot distinguish between your own healthy tissues and foreign particles, causing the body to mistakenly attack normal cells.
Researchers aren’t sure what exactly causes autoimmune diseases, but they know that it involves a combination of genetic, environmental and hormonal factors.
What Are Degenerative Joint Diseases?
Osteoarthritis is the most common form of arthritis, best described as “wear and tear” arthritis. It occurs most often in the hands, hips, and knees when the cartilage within a joint begins to break down and the underlying bone changes. If left untreated, the cartilage (protective tissue at the ends of bones) will continue to wear down, and painful symptoms will worsen over time.
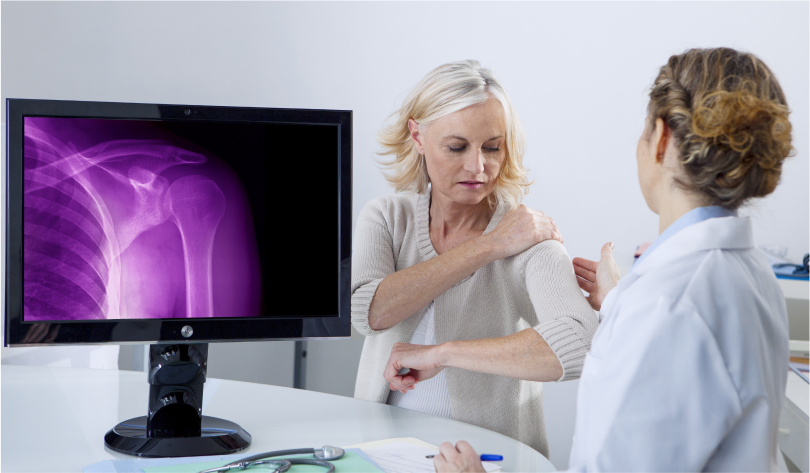
When Should You See A Rheumatologist?
Some rheumatic diseases, such as arthritis, can cause permanent joint damage. Receiving care in the earlier stages lowers your risk of developing permanent damage to your joints and organs.
You should see a rheumatologist if you have chronic joint or musculoskeletal pain that does not go away or reoccurs after short-term treatment. You may benefit from seeing a rheumatologist if you develop any of the following persistent symptoms:
- Episodes of joint pain, swelling, fever or skin rash
- Frequent attacks of gout
- Dermatitis
- Dry eyes or dry mouth
- Fatigue
- Hair loss (alopecia)
- Itching
- Muscle weakness
- Stiffness
- Swollen lymph nodes
Frequently Asked Questions
Rheumatoid arthritis is when the immune system attacks healthy cells, causing inflammation, swelling, and pain in several joints.
During a flare, patients experience a sudden increase in pain, stiffness, and swelling of the joints.
Although there is no cure for rheumatoid arthritis, early treatment (including medicine and lifestyle changes) can limit the impact of the condition.

 71–75 Shelton Street, Covent Garden, London, WC2H 9JQ
71–75 Shelton Street, Covent Garden, London, WC2H 9JQ +44 (0) 20 3376 1032
+44 (0) 20 3376 1032



