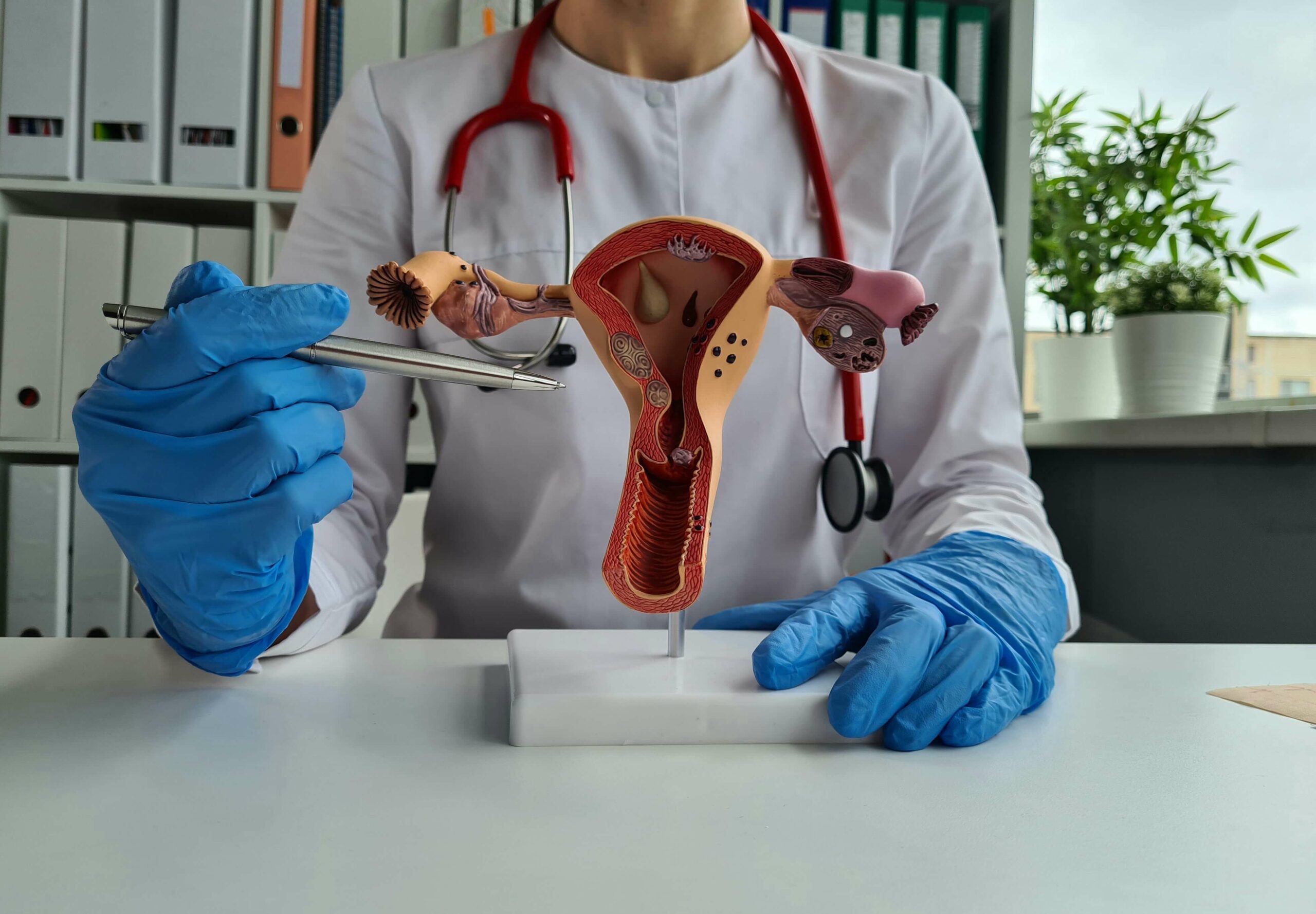
A hysterectomy procedure is a surgical operation performed to remove the uterus (or womb). The procedure is a very common surgery around the world and about one in five women will undergo a hysterectomy procedure by the age of 55. However, the number of hysterectomies is decreasing due to new, less invasive treatments becoming available to manage conditions that previously could only be cured with a hysterectomy.
Any woman of legal age can consent to the procedure although it is unlikely that a doctor will perform a hysterectomy on women ages 18-35 unless medically justified. A hysterectomy is a major operation which carries possible physical and emotional risks and should not be considered lightly.
Why Is A Hysterectomy Performed?
A hysterectomy is a major operation, with a long recovery time, and should only be considered after less invasive treatments have been tried. Hysterectomies are performed to treat health problems that affect the female reproductive system. Reasons may include:
Abnormal Or Heavy Periods
Hysterectomy can effectively eliminate heavy bleeding in cases where other treatments have not worked, or bleeding has a profound impact on a woman's life.
Pelvic Pain
Long-term pelvic pain and severe pain when menstruating can result from a variety of conditions, including endometriosis, ovarian cysts, uterine fibroids or cancer.
Fibroids
Uterine fibroids are noncancerous growths that form in the uterus. They are one of the most common reasons for a hysterectomy. Fibroids can cause heavy bleeding, pain, or stomach distention.
Uterine Prolapse
Uterine prolapse - when the uterus has “dropped” into your vaginal canal due to weakened support muscles). Common symptoms of uterine prolapse include pelvic pressure, urinary issues and bowel problems.
Hyperplasia
Endometrial hyperplasia is a condition where the lining of your uterus is abnormally thick. It causes heavy menstrual bleeding.
Recurrent Uterine Polyps
Uterine polyps, also known as endometrial polyps, form because of cells in the lining of the uterus (endometrium) overgrowing. These polyps are usually benign, although some can be precancerous or cancerous.
Adenomyosis
This condition occurs when the lining of the uterus grows into the muscle of the uterus. This causes the uterine wall to thicken, which leads to pain and heavy bleeding. This condition usually goes away after menopause, but if your symptoms are severe, you may require treatment sooner.
Severe Endometriosis
This occurs when pieces of the tissue that line the uterus (endometrium) are found outside the uterus in the fallopian tubes, ovaries, bladder, bowel, vagina or rectum.
In cases of severe endometriosis, a hysterectomy may be needed to remove the uterus along with the ovaries and fallopian tubes. Doctors usually recommend hormone therapy or medical procedures to remove endometrial tissue before a hysterectomy.
Cancer
Cancer is the reason for about 10 per cent of all hysterectomies. Cancers of the reproductive system include ovarian cancer, uterine cancer, cervical cancer, or cancer of the fallopian tubes. Sometimes, doctors recommend surgery if you have precancerous conditions. Some women who have Lynch syndrome opt to have a hysterectomy to reduce their risk of developing cancer in the future. This is an inherited condition t hat can increase your risk of colon, and uterine cancer.
People who have the BRCA gene may have an increased risk for ovarian and breast cancers. A hysterectomy is not always necessary although doctors often recommend the removal of the ovaries and fallopian tubes.
Gender Affirmation
Transgender people and people who are nonbinary may elect to have a hysterectomy to affirm their gender identity.
What Are the Benefits Of Having A Hysterectomy?
Having a hysterectomy can improve your quality of life, especially if you have constant pelvic pain or heavy and irregular bleeding. A hysterectomy can also be lifesaving if you are at risk of developing uterine cancer.
A hysterectomy should not affect your sex life. Having the procedure will not change the sensation in your vagina or your ability to have an orgasm. However, if your ovaries were removed during the procedure, it could affect your sex drive due to the onset of menopause.
What Are The Disadvantages of Having A Hysterectomy?
A hysterectomy is a major surgery with a long recovery and comes with risks and side effects. It is permanent and you will not be able to fall pregnant afterwards. This can cause depression and psychological stress in some women.
If your ovaries were removed at the time of your hysterectomy, you can become menopausal and experience symptoms such as hot flushes, vaginal dryness, loss of libido and insomnia (difficulty sleeping).
Although uncommon, complications during surgery can include infection, haemorrhaging, or bladder or bowel damage. In the long term, it can increase the risk of stroke, bone loss, heart attacks, urinary issues, and early-onset menopause in younger women.

 71–75 Shelton Street, Covent Garden, London, WC2H 9JQ
71–75 Shelton Street, Covent Garden, London, WC2H 9JQ +44 (0) 20 3376 1032
+44 (0) 20 3376 1032



